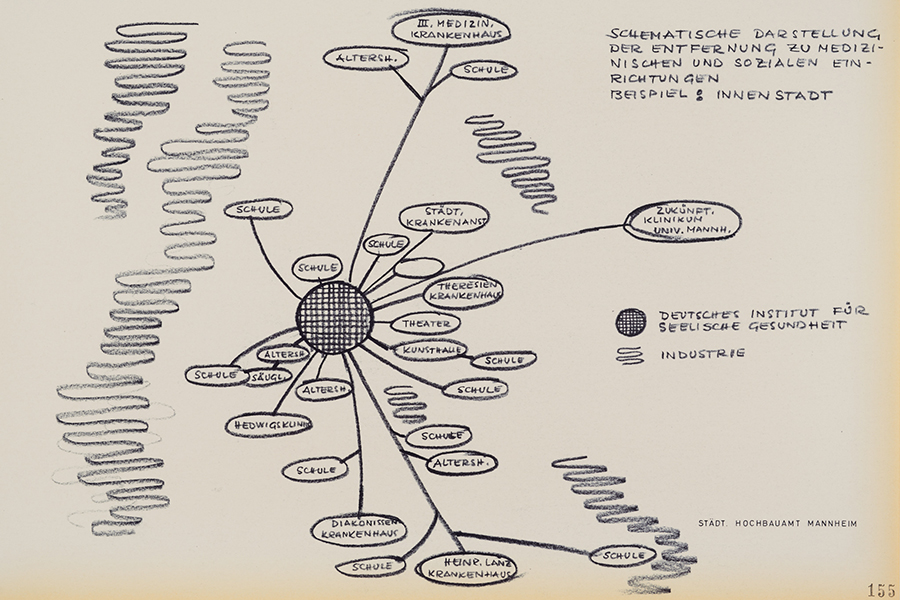
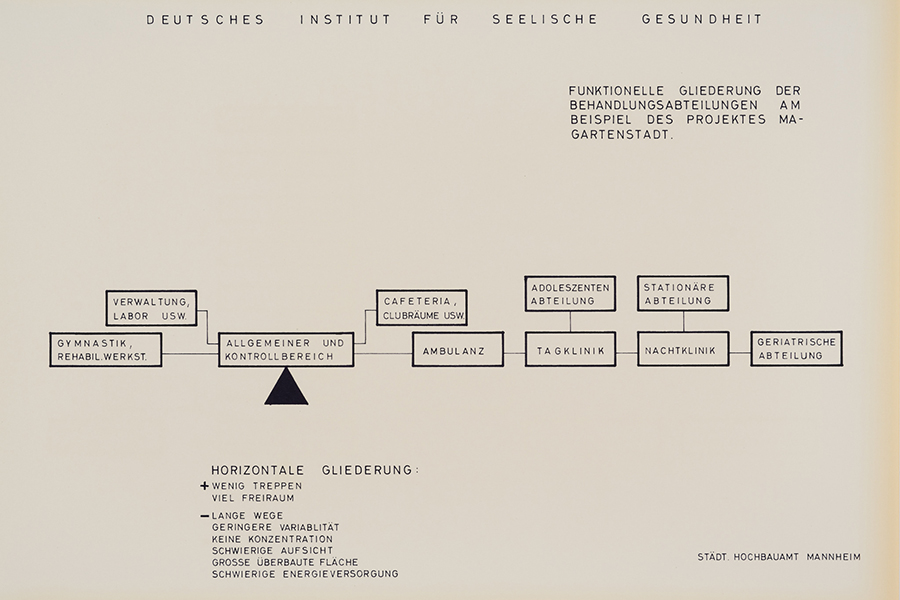
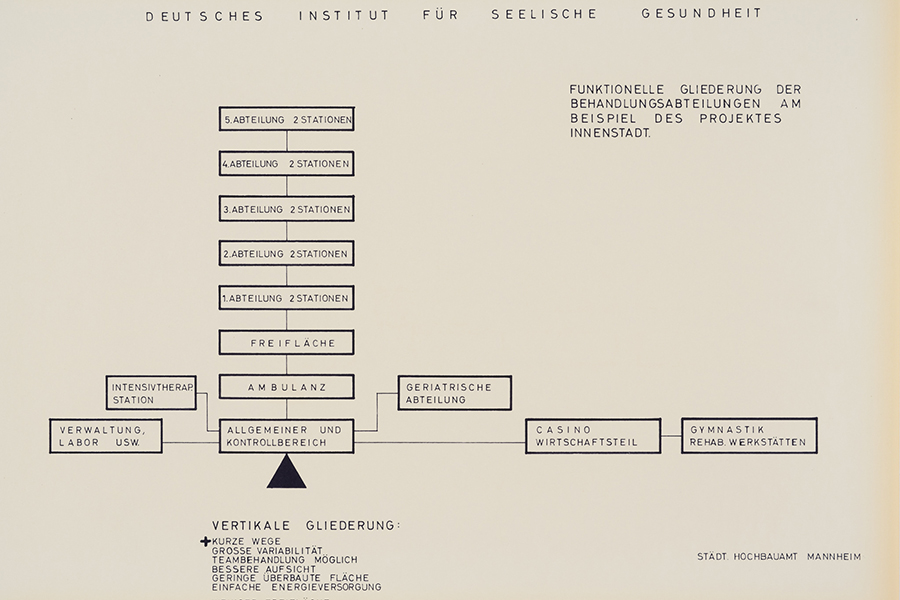
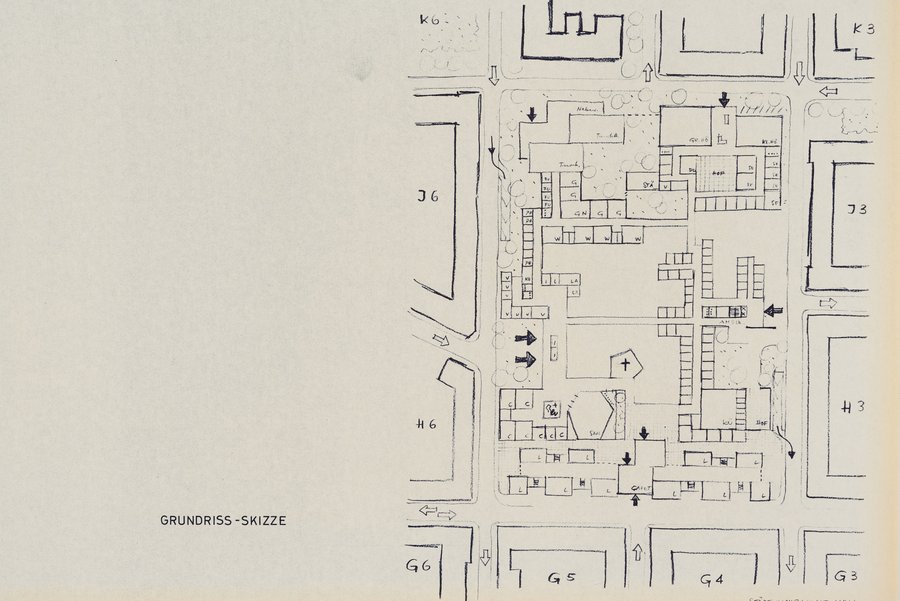
There are many milestones on a 50-year journey. Join us on an exciting journey through the history of the CIMH!
To the beginningDecember 2024
Dr. Gordon Feld has been awarded the ERC Consolidator Grant, which is endowed with around two million euros, for his research into memory processing during sleep using state-of-the-art imaging.
October 2024
The CIMH is involved in the Collaborative Research Centre TRR 379 Neuropsychobiology of Aggression. Funding amount EUR 16 million. This TRR is investigating the biological basis of different forms of aggression.
May 2024
Further funding from the Dietmar Hopp Foundation and funds from the state of Baden-Württemberg are making the second phase of the Stark im Sturm project possible. The project will be extended to other psychiatric clinics in Baden-Württemberg.
May 2024
Prof Dr Christian Schmahl accepts the appointment to the Chair of Psychosomatics and Psychotherapeutic Medicine at Heidelberg University and becomes Medical Director of the Clinic for Psychosomatics and Psychotherapeutic Medicine at the CIMH.
April 2024
Senior Professor Prof. Dr Dr h.c. Dr h.c. Herta Flor receives an ERC Advanced Grant for her research project on a mechanism-based approach to the prevention of chronic pain and associated mental disorders (MECHPAIN).
March 2024
The Baden-Württemberg Ministry of Science, Research and the Arts is increasing its funding for the 3R Centre Rhine-Neckar.
March 2024
The CIMH becomes a partner of European Brain Research Infrastructures (EBRAINS), an EU digital research infrastructure that combines neuroscience and medicine with AI and computer technology.
January 2024
The research network for the investigation of sexualised violence and other forms of abuse in the Protestant Church and Diaconia in Germany (FORUM) has published its results. The CIMH was involved with a sub-project headed by Prof Dr Harald Dreßing.
September 2023
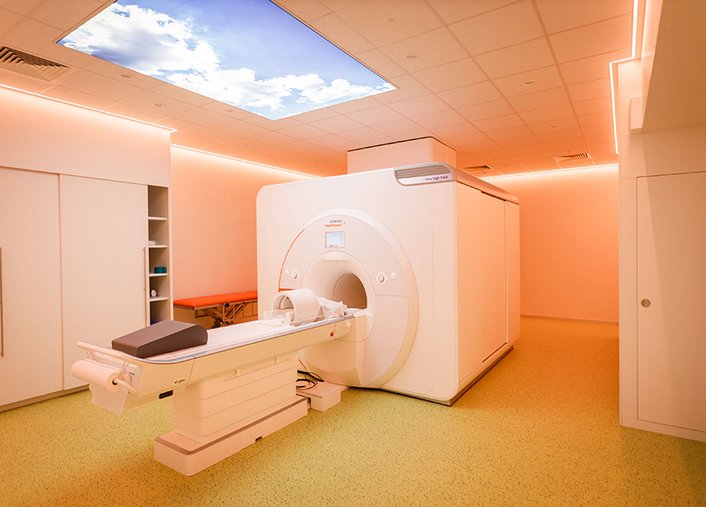
Thanks to the support of the Klaus Tschira Foundation, the CIMH is able to purchase a 7 Tesla magnetic resonance tomograph.
May 2023
The German Centre for Mental Health begins its work. The CIMH co-ordinates one of six locations and provides one of the founding spokespersons, Prof. Dr Andreas Meyer-Lindenberg.
May 2023
The Collaborative Research Centres SFB 1158 on pain and TRR 265 on addictive disorders, in which the CIMH is involved, are being extended.
May 2023
The Baden-Württemberg-Stiftung is funding the project Elternsein motiviert und abstinent (ELMA). An app is being developed to accompany therapy for parents suffering from addiction.
April 2023
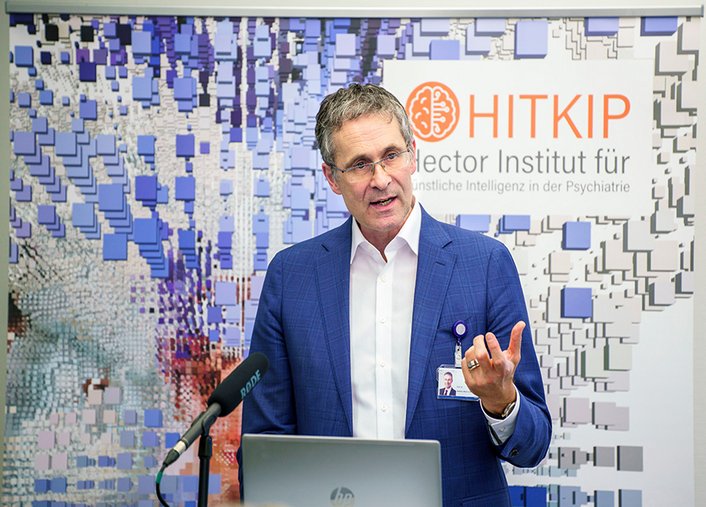

The Hector Institute for Artificial Intelligence in Psychiatry (HITKIP) is opened in the presence of Science Minister Petra Olschowski and the founders Dr Hans-Werner and Josephine Hector. The aim of research at HITKIP is to develop and apply innovative computational methods from the field of artificial intelligence in order to uncover the causes of mental illness.
January 2023
Prof. Dr Andreas Meyer-Lindenberg becomes President of the German Society for Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Psychosomatics and Neurology.
2023
ERC Synergy Grant for the project Oxytocin-driven spatial mapping in the mammalian hippocampal formation by Prof Dr Valery Grinevich. Funding amount EUR 10 million. The international research team is investigating the neuronal basis of humans' ability to process spatial geometry in terms of space ownership, utility value and social hierarchies.
November 2022
The Federal Ministry of Education and Research has approved a further 2.6 million euros for the EPIsoDE psilocybin depression study.
December 2021
The CIMH will be part of the Health + Life Science Alliance Heidelberg Mannheim, which is supported by the state of Baden-Württemberg.
September 2021
The Stark im Sturm initiative, founded at the CIMH with funding from the Dietmar Hopp Foundation, establishes child counsellors in clinics in the region to promote support for parents with mental health or addiction problems and their children.
March 2021
The ZIHUb research alliance, consisting of researchers from the ZI and the universities of Heidelberg and Ulm, has qualified to design the new German Centre for Mental Health together with other selected research locations from mid-2021.
March 2021

Funded by the Baden-Württemberg Ministry of Science, Research and the Arts, the 3R Centre Rhine-Neckar is being launched as a collaboration between the CIMH, University Medicine Mannheim and Heidelberg University, coordinated by the CIMH. The aim is to further advance the commitment to animal welfare in research in accordance with the internationally recognised 3Rs principle.
November 2020

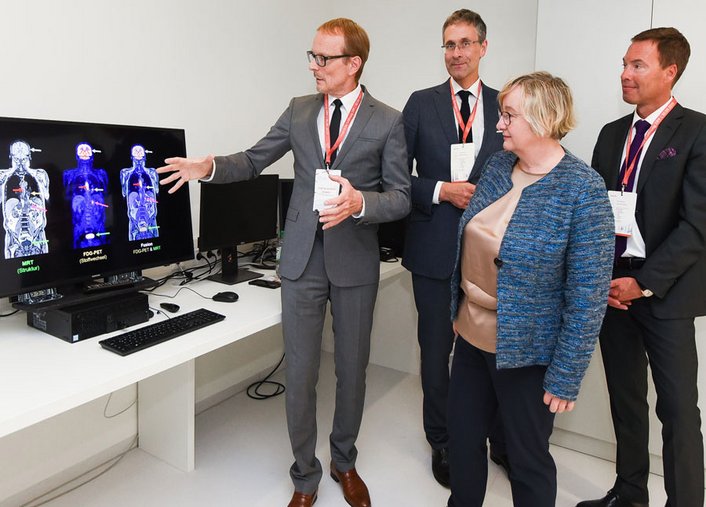
The EPIsoDE study, funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research and led by Prof Dr Gerhard Gründer, is investigating the efficacy and safety of the psychedelic substance psilocybin in the treatment of depression at the Mannheim and Berlin sites. EPIsoDE is the largest study with psilocybin in Europe to date.
October 2020
The CIMH introduces the concept of first aid for mental illness in Germany. The Mental Health First Aid (MHFA) courses teach people how to recognise symptoms and how to approach and support those affected. They also break down prejudices against people with mental health problems.
September 2019

After several years of renovation work in the therapy building, the Centre for Innovative Psychiatry and Psychotherapy Research (ZIPP) is opened. The CIMH is pooling and expanding its technical research infrastructure in the immediate vicinity of the clinic.
August 2019

The second adolescent centre is opened. Adolescents and young adults with psychotic symptoms are cared for and treated there according to the Soteria concept.
May 2019
The CIMH is involved in the Collaborative Research Centre TRR 265 Loss and Regaining Control in Addictive Disorders. Spokesperson since 2023 is Prof Dr Rainer Spanagel. Funding amount to date EUR 29.4 million. The CRC investigates the mechanisms that cause people to lose control over drug use.
March 2019
The CIMH establishes a patient advisory board to promote dialogue between researchers and experts and their relatives.
September 2018
Prof Dr Harald Dreßing, Head of Forensic Psychiatry at the CIMH, presents the results of a study on the abuse of minors under the responsibility of the German Bishops' Conference (MHG study).
July 2018
The Hector Institute for Translational Brain Research (HITBR) is founded as a joint project of the CIMH, the German Cancer Research Centre and the Hector Foundation II. The aim is to use stem cell research to find new molecular and functional starting points for the treatment of severe psychiatric illnesses.
December 2017
The CIMH participates in the Research Training Group GRK 2350 on the influence of trauma in childhood and adolescence on psychosocial and somatic diseases across the lifespan. Spokesperson: Prof Dr Christian Schmahl, funding amount EUR 5 million.
2017
The first track unit is opened at the CIMH. Tracks specialise in one or more mental illnesses and – unlike traditional wards – offer outpatient, day-care and inpatient treatment options, including acute care. This bundling enables chronic mental illnesses to be treated better and more individually in the long term.
February 2017
The CIM establishes the Feuerlein Centre for Translational Addiction Medicine in cooperation with the North Baden Psychiatric Centre.
2016
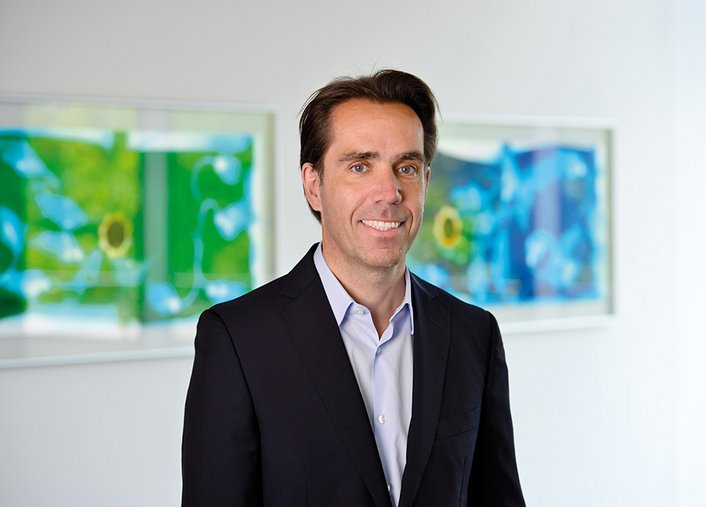

Prof. Dr Falk Kiefer becomes Medical Director of the Clinic for Addictive Behaviour and Addiction Medicine and holds the Chair of Addiction Research.
March 2016
The CIMH coordinates the international research consortium Systems Biology of Alcohol Addiction (SyBil-AA) to investigate the neurobiological causes of relapse in alcohol addiction. The EU is funding the consortium with 5.7 million euros.
January 2016
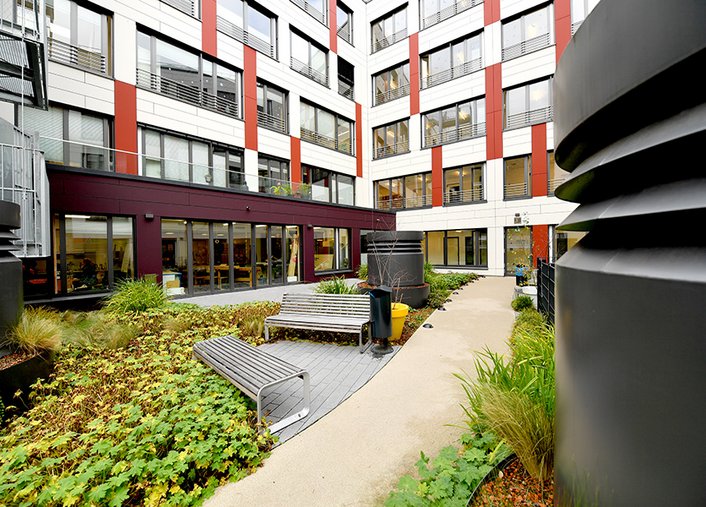

The new building in K 3 is completed and the first adolescent centre in Germany for adolescents and young adults with borderline personality disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder is opened there.
June 2015
The CIMH is involved in the new Collaborative Research Centre SFB 1158 From Nociception to Chronic Pain via Prof. Dr Dr h. c. h. c. Herta Flor. Funding amount EUR 45.2 million. The SFB is investigating how acute pain develops into chronic pain.
February 2014
The CIMH coordinates the two joint projects ESPRIT (schizophrenia) and ESCA (ADHD) funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
2013
The Psychoepidemiological Centre at the CIMH brings together research activities in the fields of epidemiology, health services research and health economics with neurobiological methods (imaging, genetics, epigenetics, neuropsychology, virtual reality) and research groups.
2013
The RELEASE collaborative study, funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research and led by Prof Dr Martin Bohus, is investigating patients with post-traumatic stress disorder following experiences of violence in childhood and adolescence.
2013
Foundation of the Clinical Research Unit KFO 256 Mechanisms of Disturbed Emotion Processing in Borderline Personality Disorder under the direction of Prof Dr Christian Schmahl
2012
The CIMH is the first psychiatric hospital in Baden-Württemberg to be recognised as a self-help-friendly hospital.
2010
The Bernstein Centre for Computational Neuroscience Heidelberg-Mannheim, funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, is being established under the direction of PD Dr Daniel Durstewitz.
April 2009
A second 3 Tesla magnetic resonance tomograph is put into operation in the therapy building.
2009
ERC Advanced Grant for the research project Phantom Phenomena: A Window to the Mind and Brain (PHANTOMMIND) by Prof. Dr Dr h.c. Dr h.c. Herta Flor. Funding amount EUR 2.3 million. The project is investigating which parts of the brain are active during phantom pain, phantom sensations and physical illusions.
2007
Andreas Meyer-Lindenberg becomes Professor of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Medical Director of the Clinic for Psychiatry and Psychotherapy and Chairman of the Board of the CIMH.
2006
Prof Dr Dr Tobias Banaschewski becomes Medical Director of the Clinic for Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Psychotherapy and Deputy Director of the CIMH.
2004
The Collaborative Research Centre SFB 636 Memory and Plasticity of the Brain: Implications for Psychopathology has been approved and will run until 2016. Spokesperson: Prof. Dr. Dr. h.c. Dr h.c. Herta Flor, funding amount EUR 26.7 million. The CRC is investigating how learning and memory processes and the associated plastic changes in the brain are involved in the development of mental disorders.
October 2003
Prof. Dr Martin Bohus is appointed to the Chair of Psychosomatics and Psychotherapeutic Medicine.
February 2002
The CIMH becomes the coordination centre of the Dementia Competence Network, with Prof. Dr. Dr. Fritz Henn as spokesperson.
July 2000
The geriatric psychiatry department with 44 beds opens on the renovated seventh floor of the therapy building.
April 1999
Prof. Dr Karl Mann is appointed to the Chair of Addiction Research, the Clinic for Addictive Behaviour and Addiction Medicine is opened.
October 1994
Prof Dr Dr Fritz A. Henn succeeds Heinz Häfner as Director of the CIMH and Chair of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy.
1989
Founding of the Social Psychiatric Service (SpDi) as a central outpatient psycho-social contact point for chronically mentally ill citizens of the city of Mannheim
1987
The Collaborative Research Centre SFB 258 Indicators and Risk Models for the Development and Progression of Mental Disorders is approved and runs until 1998. Spokesperson: Prof. Dr. Dr. Martin Schmidt, funding amount DM 25.4 million. Within the framework of the SFB, various models of the development of mental disorders are being investigated.
1983
Mannheim Starthilfe is founded to promote the professional integration of mentally ill people. In cooperation with companies from the region, it offers patients the opportunity to test their skills and resilience in work trials.
April 1982
The day clinic moves from Heidelberg to Mannheim as the last part of the former social psychiatric clinic.
1980
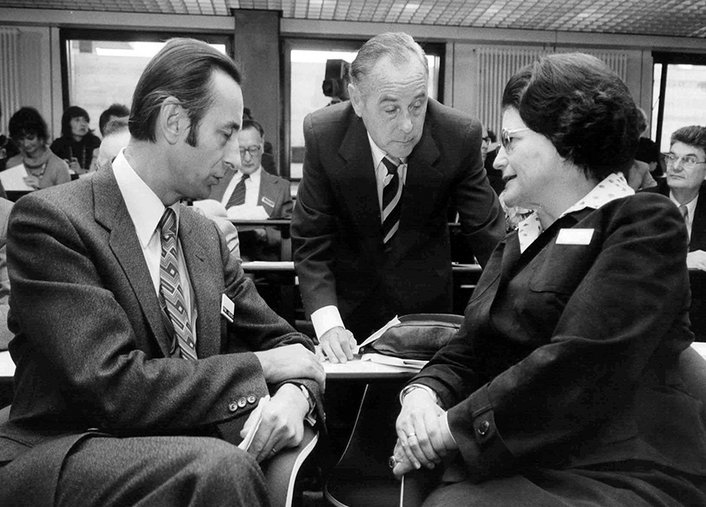

The CIMH becomes the Collaborating Centre for Training and Research in Mental Health of the World Health Organisation (WHO) and remains so until 2006. A WHO conference was held at the CIMH as early as 1976. The topic was the participation of former psychiatric patients and their relatives in the planning and practice of psychiatric care.
How the CIMH started business
- 3 clinics: psychiatry (100 treatment places), psychosomatic medicine and psychotherapy (44), child and adolescent psychiatry (50)
- 6 departments: Clinical Psychology, Epidemiological Psychiatry, Community Psychiatry and Mental Hygiene, Psychotherapeutic Outpatient Clinic for Children and Adolescents, Medical Sociology and Biostatistics
- 173 employees
Quotes on the founding of the CIMH
‘The Central Institute is ‘an unusual, original and thoroughly convincing solution (...). It is not simply an addition to the existing university clinics, but a very sensible combination of institutional research with clinical and healthcare tasks.’
Prof Dr Caspar Kuhlenkampff, Chairman of the Expert Commission on Psychiatry (Enquête Commission)
‘I am impressed by the way your institute takes research in partnership with the community, the city and the university (...) seriously. This is also the reason why I am convinced that the pioneering work of the Institute will be successful and of great importance for German psychiatry and probably also for world psychiatry.’
Prof Dr Fritz Redlich, Connecticut Mental Health Center and Yale University, Department of Psychiatry
‘It really was a march through the institutions: a very, very long march.’
Dr Hans Martini, mayor and foundation representative
September 1975
Prof. Dr Dr Martin Schmidt is appointed to the Chair of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and becomes Medical Director of the Clinic for Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.
May 23/24, 1975
The statutes of the CIMH are published in the Baden-Württemberg Law Gazette and come into force.
April 8, 1975
The state foundation under public law, the Central Institute of Mental Health, is established in Mannheim.
1975
While the interior of the building is still being completed, various departments gradually move into the new building.
1975
Prof Dr Dr Heinz Schepank is appointed to the Chair of Psychosomatic Medicine and Psychotherapy and becomes Medical Director of the Psychosomatic Clinic at the CIMH.
1975
Prof Dr Dr Heinz Häfner becomes Director of the Psychiatric Clinic and Chairman of the Foundation of the CIMH.
1975
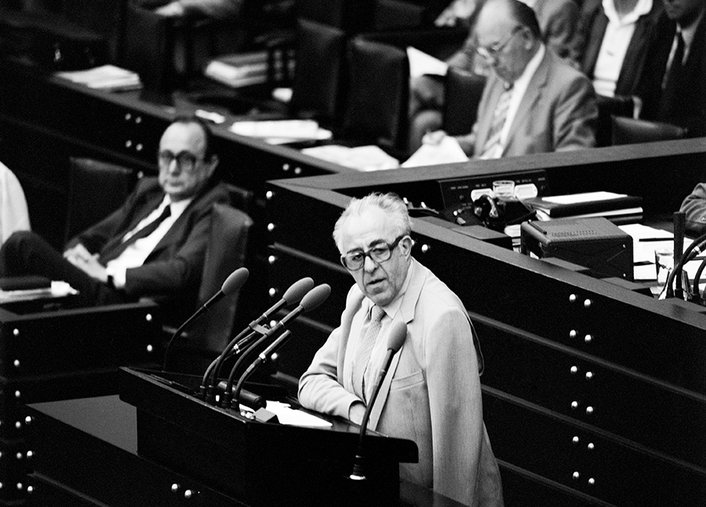

The report on the situation of psychiatry in the Federal Republic of Germany is presented.
1974
Dr Niels Pörksen, Head of the Department of Community Psychiatry at the CIMH, publishes the book Community Psychiatry. The Mannheim Model.
1973/74
At the turn of the year 1973/74, the Social Psychiatric Clinic moves with 55 beds from Heidelberg to the Mannheim Municipal Hospitals.
1973
The Collaborative Research Centre SFB 116 Psychiatric Epidemiology is approved and runs until 1985. Spokesperson: Prof. Dr. Dr. h. c. Heinz Häfner, Prof. Dr. Dr. Martin Schmidt, funding amount DM 18.5 million. The SFB deals with epidemiological incidence and prevalence studies - i.e. where and how often mental illnesses occur -, health care research and the development of methods.
1971
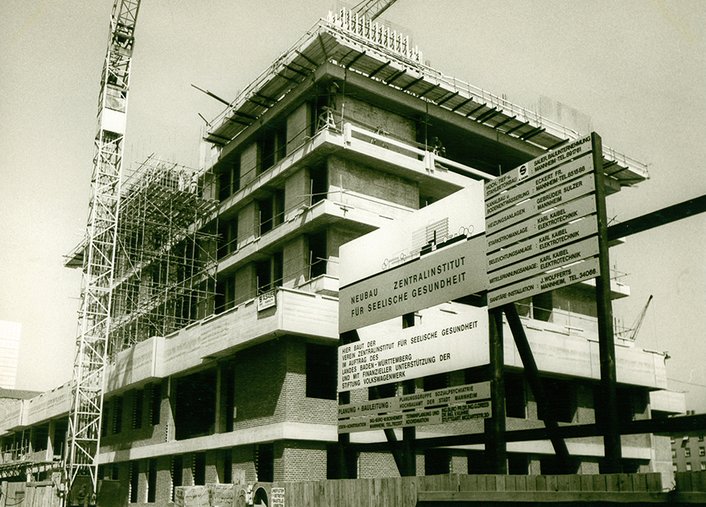
After the Volkswagenwerk Foundation had provided DM 7.55 million, the federal government assumed two thirds of the remaining construction and equipment costs (DM 21 million) and the state of Baden-Württemberg one third (DM 10.5 million).
1969
Heinz Häfner and colleagues publish figures on the frequency of mental illnesses in Mannheim for the first time.
November 1969
The Volkswagenwerk Foundation provides DM 7.55 million as start-up aid for the preparation and establishment of the Institute.
May 1969
In a report, the German Council of Science and Humanities ‘urgently’ recommends the establishment of the planned model institute. It proposes the name Central Institute for Mental Health - Model Institute for Psychiatry.
1969

The Community Psychiatry Working Group is founded at the Social Psychiatric Clinic in Mannheim. From 1975, it becomes the Department of Community Psychiatry at the CIMH.
1968
The planning is concretised
The Mannheim City Planning Office submits a ‘structural analysis and preparatory studies’ for the German Institute of Mental Health.
1968
Heinz Häfner becomes Chair of Psychiatry
Prof Dr Dr Heinz Häfner is appointed to the Chair of Psychiatry at the Faculty of Clinical Medicine in Mannheim at the University of Heidelberg and heads the new Social Psychiatric Clinic.
From 1968
A socio-psychiatric movement emerges throughout Germany
From 1968 onwards, criticism of the state of psychiatry and dissatisfaction with working conditions prompted employees from all professional groups in psychiatry throughout Germany to join forces in order to change the situation in psychiatry. The first supra-regional meeting took place in Mannheim in May 1970. The ‘Mannheim Circle’ came to epitomise the social psychiatry movement.
From the Mannheim Circle to the German Society for Social Psychiatry
50 years of fighting for humane psychiatry
1967
A first step towards Mannheim
The Heidelberg Social Psychiatric Clinic opens a social psychiatric outpatient clinic on the premises of the Mannheim Municipal Hospitals.
1966 and 1967

On site with the role models
Häfner, Martini and Reschke travelled to the USA, Canada and Great Britain together with architects from the Mannheim Building Department to obtain inspiration for the planning of the CIMH from psychiatric facilities.
October 1966
The state parliament of Baden-Württemberg decides to support the planned German Institute for Mental Health.
1966
Planning funds enable study trips
The Volkswagenwerk Foundation grants the association planning funds amounting to DM 120,000. Now things can continue, including study trips to psychiatric institutions abroad.
1965
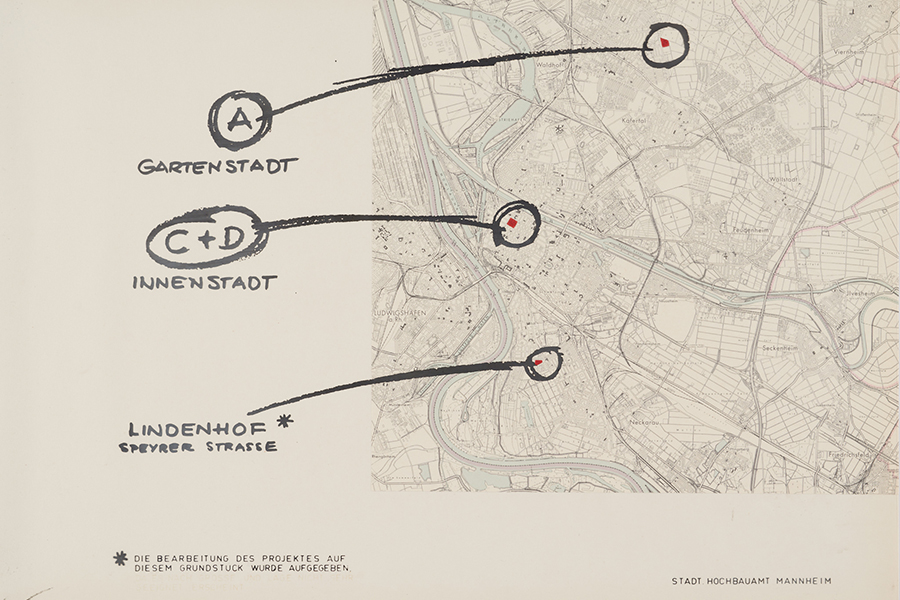
Mannheim is chosen as the location
The city of Heidelberg is unable to offer a site for the construction of a model institute. Mannheim seizes the opportunity.
1965

Häfner and colleagues publish a memorandum
Together with von Baeyer and Kisker, Häfner publishes the memorandum Urgent reforms in psychiatric care in the Federal Republic of Germany. In it, he describes the current situation as a “national emergency”.
1965
Häfner can open a social psychiatry department
Success after two years: The Baden-Württemberg Ministry of Education and Cultural Affairs approves the establishment of the Department of Social Psychiatry and Rehabilitation in Heidelberg requested by Häfner. Prof. von Baeyer provides two pavilions and staff positions at his clinic in Heidelberg for this purpose.
1965
A support association becomes the new basis for action
The Association for the Establishment and Promotion of the Model Institute for Social Psychiatric Therapy and Research is founded. In the near future, all further activities will emanate from this association.
1964
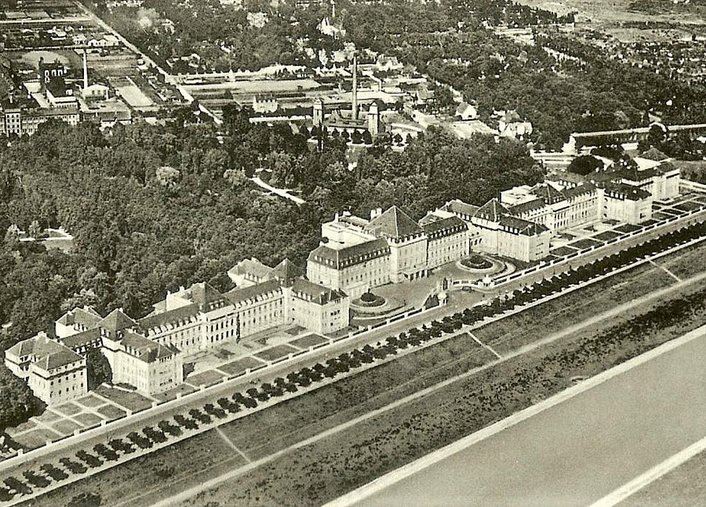
The Faculty of Clinical Medicine Mannheim at Heidelberg University is founded.
History of the Faculty of Medicine Mannheim
1964
Contacts with politicians
Heinz Häfner presents plans for psychiatric reform in Germany and for a model institute at the Federal Ministry of Health.
1963
No good care without qualified nursing staff
On the initiative of Heinz Häfner, the first training centre in Germany is founded in Heidelberg, where nurses can train to become psychiatric specialists while working.
1963

Will Heidelberg have a department for social psychiatry?
PD Dr Dr Heinz Häfner, a doctor working in clinical practice and research at the Heidelberg University Hospital for Psychiatry, applies for the establishment of a Department of Social Psychiatry and Rehabilitation. He also concretises his plans for a model institute for social psychiatric research and therapy. His superior, clinic director Prof Dr Walter Ritter von Baeyer, supported his colleague's initiatives from the outset.
1960s
The first initiatives suggested a comprehensive psychiatric reform that would rebuild psychiatric research in Germany and modernise psychiatric care.
Zentralinstitut für Seelische Gesundheit (ZI) - https://www.zi-mannheim.de